Config VPC¶
Kube-OVN supports multi-tenant isolation level VPC networks. Different VPC networks are independent of each other and can be configured separately with Subnet CIDRs, routing policies, security policies, outbound gateways, EIP, etc.
VPC is mainly used in scenarios where there requires strong isolation of multi-tenant networks and some Kubernetes networking features conflict under multi-tenant networks. For example, node and pod access, NodePort functionality, network access-based health checks, and DNS capabilities are not supported in multi-tenant network scenarios at this time. In order to facilitate common Kubernetes usage scenarios, Kube-OVN has a special design for the default VPC where the Subnet under the VPC can meet the Kubernetes specification. The custom VPC supports static routing, EIP and NAT gateways as described in this document. Common isolation requirements can be achieved through network policies and Subnet ACLs under the default VPC, so before using a custom VPC, please make sure whether you need VPC-level isolation and understand the limitations under the custom VPC.
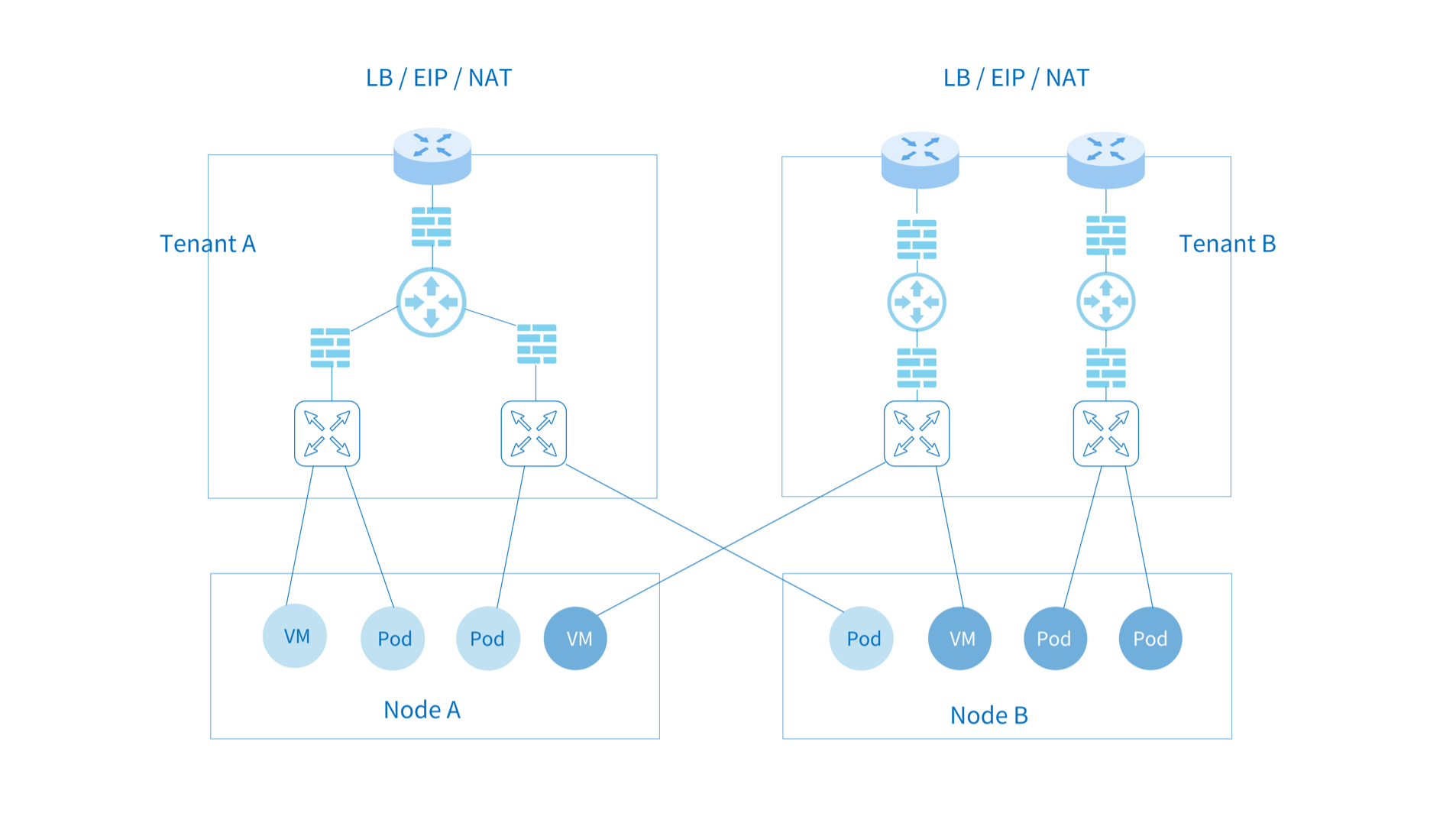
Creating Custom VPCs¶
Create two VPCs:
kind: Vpc
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: test-vpc-1
spec:
namespaces:
- ns1
---
kind: Vpc
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: test-vpc-2
spec:
namespaces:
- ns2
namespaces: Limit which namespaces can use this VPC. If empty, all namespaces can use this VPC. Create two Subnets, belonging to two different VPCs and having the same CIDR:
kind: Subnet
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: net1
spec:
vpc: test-vpc-1
cidrBlock: 10.0.1.0/24
protocol: IPv4
namespaces:
- ns1
---
kind: Subnet
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: net2
spec:
vpc: test-vpc-2
cidrBlock: 10.0.1.0/24
protocol: IPv4
namespaces:
- ns2
Create Pods under two separate Namespaces:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
annotations:
ovn.kubernetes.io/logical_switch: net1
namespace: ns1
name: vpc1-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: vpc1-pod
image: nginx:alpine
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
annotations:
ovn.kubernetes.io/logical_switch: net2
namespace: ns2
name: vpc2-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: vpc2-pod
image: nginx:alpine
After running successfully, you can observe that the two Pod addresses belong to the same CIDR, but the two Pods cannot access each other because they are running on different tenant VPCs.
Create VPC NAT Gateway¶
Subnets under custom VPCs do not support distributed gateways and centralized gateways under default VPCs.
Pod access to the external network within the VPC requires a VPC gateway, which bridges the physical and tenant networks and provides floating IP, SNAT and DNAT capabilities.
The VPC gateway function relies on Multus-CNI function, please refer to multus-cni.
Configuring the External Network¶
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
kind: Subnet
metadata:
name: ovn-vpc-external-network
spec:
protocol: IPv4
provider: ovn-vpc-external-network.kube-system
cidrBlock: 192.168.0.0/24
gateway: 192.168.0.1 # IP address of the physical gateway
excludeIps:
- 192.168.0.1..192.168.0.10
---
apiVersion: "k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1"
kind: NetworkAttachmentDefinition
metadata:
name: ovn-vpc-external-network
namespace: kube-system
spec:
config: '{
"cniVersion": "0.3.0",
"type": "macvlan",
"master": "eth1",
"mode": "bridge",
"ipam": {
"type": "kube-ovn",
"server_socket": "/run/openvswitch/kube-ovn-daemon.sock",
"provider": "ovn-vpc-external-network.kube-system"
}
}'
- This Subnet is used to manage the available external addresses and the address will be allocated to VPC NAT Gateway through Macvlan, so please communicate with your network management to give you the available physical segment IPs.
- The VPC gateway uses Macvlan for physical network configuration, and
masterofNetworkAttachmentDefinitionshould be the NIC name of the corresponding physical network NIC. providerformat is<NetworkAttachmentDefinition Name>.<NetworkAttachmentDefinition Namespace>.namemust beovn-vpc-external-network.
Enabling the VPC Gateway¶
VPC gateway functionality needs to be enabled via ovn-vpc-nat-gw-config under kube-system:
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: ovn-vpc-nat-gw-config
namespace: kube-system
data:
image: 'kubeovn/vpc-nat-gateway:v1.10.7'
enable-vpc-nat-gw: 'true'
image: The image used by the Gateway Pod.enable-vpc-nat-gw: Controls whether the VPC Gateway feature is enabled.
Create VPC Gateway and Set the Default Route¶
kind: VpcNatGateway
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: gw1
spec:
vpc: test-vpc-1
subnet: net1
lanIp: 10.0.1.254
selector:
- "kubernetes.io/hostname: kube-ovn-worker"
- "kubernetes.io/os: linux"
subnet: A Subnet within the VPC, the VPC Gateway Pod will uselanIpto connect to the tenant network under that subnet.lanIp: An unused IP within thesubnetthat the VPC Gateway Pod will eventually use for the Pod.selector: Node selector for the VPC Gateway Pod.nextHopIP: Needs to be the same aslanIp.
Create EIP¶
EIP allows for floating IP, SNAT, and DNAT operations after assigning an IP from an external network segment to a VPC gateway.
Randomly assign an address to the EIP:
kind: IptablesEIP
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: eip-random
spec:
natGwDp: gw1
Fixed EIP address assignment:
kind: IptablesEIP
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: eip-static
spec:
natGwDp: gw1
v4ip: 10.0.1.111
Create DNAT Rules¶
kind: IptablesEIP
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: eipd01
spec:
natGwDp: gw1
---
kind: IptablesDnatRule
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: dnat01
spec:
eip: eipd01
externalPort: '8888'
internalIp: 10.0.1.10
internalPort: '80'
protocol: tcp
Create SNAT Rules¶
---
kind: IptablesEIP
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: eips01
spec:
natGwDp: gw1
---
kind: IptablesSnatRule
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: snat01
spec
eip: eips01
internalCIDR: 10.0.1.0/24
Create Floating IP¶
---
kind: IptablesEIP
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: eipf01
spec:
natGwDp: gw1
---
kind: IptablesFIPRule
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: fip01
spec:
eip: eipf01
internalIp: 10.0.1.5
Custom Routing¶
Within the custom VPC, users can customize the routing rules within the VPC and combine it with the gateway for more flexible forwarding. Kube-OVN supports static routes and more flexible policy routes.
Static Routes¶
kind: Vpc
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: test-vpc-1
spec:
staticRoutes:
- cidr: 0.0.0.0/0
nextHopIP: 10.0.1.254
policy: policyDst
- cidr: 172.31.0.0/24
nextHopIP: 10.0.1.253
policy: policySrc
policy: Supports destination routingpolicyDstand source routingpolicySrc.- When there are overlapping routing rules, the rule with the longer CIDR mask has higher priority, and if the mask length is the same, the destination route has a higher priority over the source route.
Policy Routes¶
Traffic matched by static routes can be controlled at a finer granularity by policy routing. Policy routing provides more precise matching rules, priority control and more forwarding actions. This feature brings the OVN internal logical router policy function directly to the outside world, for more information on its use, please refer to Logical Router Policy.
A example of policy routes:
kind: Vpc
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
metadata:
name: test-vpc-1
spec:
policyRoutes:
- action: drop
match: ip4.src==10.0.1.0/24 && ip4.dst==10.0.1.250
priority: 11
- action: reroute
match: ip4.src==10.0.1.0/24
nextHopIP: 10.0.1.252
priority: 10
Created: June 30, 2022