Underlay Installation¶
By default, the default subnet uses Geneve to encapsulate cross-host traffic, and build an overlay network on top of the infrastructure.
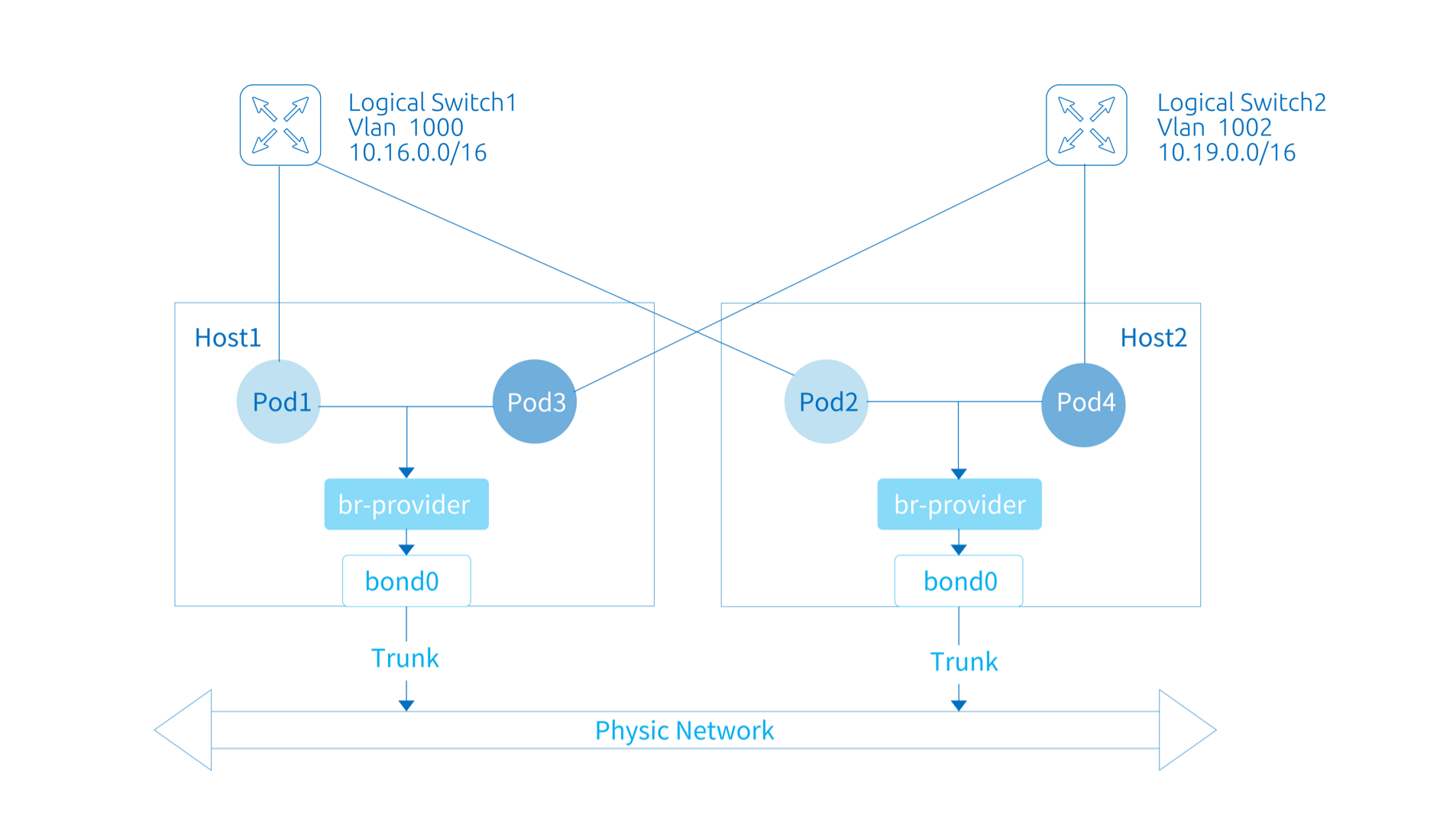
For the case that you want the container network to use the physical network address directly, you can set the default subnet of Kube-OVN to work in Underlay mode, which can directly assign the address resources in the physical network to the containers, achieving better performance and connectivity with the physical network.
Limitation¶
Since the container network in this mode uses physical network directly for L2 packet forwarding, L3 functions such as SNAT/EIP, distributed gateway/centralized gateway in Overlay mode cannot be used. VPC level isolation is also not available for underlay subnet.
Comparison with Macvlan¶
The Underlay mode of Kube-OVN is very similar to the Macvlan, with the following major differences in functionality and performance:
- Macvlan performs better in terms of throughput and latency performance metrics due to its shorter kernel path and the fact that it does not require OVS for packet processing.
- Kube-OVN provides arp-proxy functionality through flow tables to mitigate the risk of arp broadcast storms on large-scale networks.
- Since Macvlan works at the bottom of the kernel and bypasses the host netfilter, Service and NetworkPolicy functionality requires additional development. Kube-OVN provides Service and NetworkPolicy capabilities through the OVS flow table.
- Kube-OVN Underlay mode provides additional features such as address management, fixed IP and QoS compared to Macvlan.
Environment Requirements¶
In Underlay mode, the OVS will bridge a node NIC to the OVS bridge and send packets directly through that node NIC, relying on the underlying network devices for L2/L3 level forwarding capabilities. You need to configure the corresponding gateway, Vlan and security policy in the underlying network device in advance.
- For OpenStack VM environments, you need to turn off
PortSecurityon the corresponding network port. - For VMware vSwitch networks,
MAC Address Changes,Forged TransmitsandPromiscuous Mode Operationshould be set toallow. - For Hyper-V virtualization,
MAC Address Spoofingshould be enabled in VM nic advanced features. - Public clouds, such as AWS, GCE, AliCloud, etc., do not support user-defined Mac, so they cannot support Underlay mode network. In this scenario, if you want to use Underlay, it is recommended to use the VPC-CNI provided by the corresponding public cloud vendor..
- The network interface that is bridged into ovs can not be type of Linux Bridge.
For management and container networks using the same NIC, Kube-OVN will transfer the NIC's Mac address, IP address, route, and MTU to the corresponding OVS Bridge to support single NIC deployment of Underlay networks. OVS Bridge name format is br-PROVIDER_NAME,PROVIDER_NAME is the name of ProviderNetwork (Default: provider).
Specify Network Mode When Deploying¶
This deployment mode sets the default subnet to Underlay mode, and all Pods with no subnet specified will run in the Underlay network by default.
Download Script¶
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubeovn/kube-ovn/release-1.11/dist/images/install.sh
Modify Configuration Options¶
NETWORK_TYPE # set to vlan
VLAN_INTERFACE_NAME # set to the NIC that carries the Underlay traffic, e.g. eth1
VLAN_ID # The VLAN Tag need to be added,if set 0 no vlan tag will be added
POD_CIDR # The Underlay network CIDR, e.g. 192.168.1.0/24
POD_GATEWAY # Underlay physic gateway address, e.g. 192.168.1.1
EXCLUDE_IPS # Exclude ranges to avoid conflicts between container network and IPs already in use on the physical network, e.g. 192.168.1.1..192.168.1.100
Run the Script¶
bash install.sh
Dynamically Create Underlay Networks via CRD¶
This approach dynamically creates an Underlay subnet that Pod can use after installation.
Create ProviderNetwork¶
ProviderNetwork provides the abstraction of host NIC to physical network mapping, unifies the management of NICs belonging to the same network, and solves the configuration problems in complex environments with multiple NICs on the same machine, inconsistent NIC names and inconsistent corresponding Underlay networks.
Create ProviderNetwork as below:
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
kind: ProviderNetwork
metadata:
name: net1
spec:
defaultInterface: eth1
customInterfaces:
- interface: eth2
nodes:
- node1
excludeNodes:
- node2
Note: The length of the ProviderNetwork resource name must not exceed 12.
defaultInterface: The default node NIC name. When the ProviderNetwork is successfully created, an OVS bridge named br-net1 (in the formatbr-NAME) is created in each node (except excludeNodes) and the specified node NIC is bridged to this bridge.customInterfaces: Optionally, you can specify the NIC to be used for a specific node.excludeNodes: Optional, to specify nodes that do not bridge the NIC. Nodes in this list will be added with thenet1.provider-network.ovn.kubernetes.io/exclude=truetag.
Other nodes will be added with the following tags:
| Key | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| net1.provider-network.ovn.kubernetes.io/ready | true | bridge work finished, ProviderNetwork is ready on this node |
| net1.provider-network.ovn.kubernetes.io/interface | eth1 | The name of the bridged NIC in the node. |
| net1.provider-network.ovn.kubernetes.io/mtu | 1500 | MTU of bridged NIC in node |
If an IP has been configured on the node NIC, the IP address and the route on the NIC are transferred to the corresponding OVS bridge.
Create VLAN¶
Vlan provides an abstraction to bind Vlan Tag and ProviderNetwork.
Create a VLAN as below:
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
kind: Vlan
metadata:
name: vlan1
spec:
id: 0
provider: net1
id: VLAN ID/Tag,Kube-OVN will add this Vlan tag to traffic, if set 0, no tag is added.provider: The name of ProviderNetwork. Multiple VLAN can use a same ProviderNetwork.
Create Subnet¶
Bind Vlan to a Subnet as below:
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
kind: Subnet
metadata:
name: subnet1
spec:
protocol: IPv4
cidrBlock: 172.17.0.0/16
gateway: 172.17.0.1
vlan: vlan1
Simply specify the value of vlan as the name of the VLAN to be used. Multiple subnets can refer to the same VLAN.
Create Pod¶
You can create containers in the normal way, check whether the container IP is in the specified range and whether the container can interoperate with the physical network.
For fixed IP requirements, please refer to Fixed Addresses
Logical Gateway¶
For cases where no gateway exists in the physical network, Kube-OVN supports the use of logical gateways configured in the subnet in Underlay mode. To use this feature, set spec.logicalGateway to true for the subnet:
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
kind: Subnet
metadata:
name: subnet1
spec:
protocol: IPv4
cidrBlock: 172.17.0.0/16
gateway: 172.17.0.1
vlan: vlan1
logicalGateway: true
When this feature is turned on, the Pod does not use an external gateway, but a Logical Router created by Kube-OVN to forward cross-subnet communication.
Interconnection of Underlay and Overlay Networks¶
If a cluster has both Underlay and Overlay subnets, by default, Pods in the Overlay subnet can access the Pod IPs in the Underlay subnet via a gateway using NAT. From the perspective of Pods in the Underlay subnet, the addresses in the Overlay subnet are external, and require the underlying physical device to forward, but the underlying physical device does not know the addresses in the Overlay subnet and cannot forward. Therefore, Pods in the Underlay subnet cannot access Pods in the Overlay subnet directly via Pod IPs.
If you need to enable communication between Underlay and Overlay networks, you need to set the u2oInterconnection of the subnet to true. In this case, Kube-OVN will use an additional Underlay IP to connect the Underlay subnet and the ovn-cluster logical router, and set the corresponding routing rules to enable communication. Unlike the logical gateway, this solution only connects the Underlay and Overlay subnets within Kube-OVN, and other traffic accessing the Internet will still be forwarded through the physical gateway.
Specify logical gateway IP¶
After the interworking function is enabled, an IP from the subnet will be randomly selected as the logical gateway. If you need to specify the logical gateway of the Underlay Subnet, you can specify the field u2oInterconnectionIP.
Specify custom VPC for Underlay Subnet connection¶
By default, the Underlay Subnet will communicate with the Overlay Subnet on the default VPC. If you want to specify to communicate with a certain VPC, after setting u2oInterconnection to true, specify the subnet.spec.vpc field as the name of the VPC.
Notice¶
If there are IP addresses on the host nic, the OS you are using is Ubuntu, and the networking is configured with Netplan, it's recomanded to set NetworkManager as the renderer and to set static IP addresses for the nic (disable DHCP):
network:
renderer: NetworkManager
ethernets:
eth0:
dhcp4: no
addresses:
- 172.16.143.129/24
version: 2
If the host networking service is NetworkManager, Kube-OVN will remove the host nic from the managed devices (managed by NetworkManager is no) after creating ProviderNetwork:
root@ubuntu:~# nmcli device status
DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION
eth0 ethernet unmanaged netplan-eth0
If you want to change the host nic's IP/route configuration, you need to set the nic managed by NetworkManager manually:
nmcli device set eth0 managed yes
After setting managed to yes,Kube-OVN will transfer IP and routes on the nic to the OVS bridge, and remove the nic from the managed devices again.
Notice:If the host nic's MAC is changed, Kube-OVN will not change the OVS bridge's MAC unless kube-ovn-cni is restarted.
Known Issues¶
When the physical network is enabled with hairpin, Pod network is abnormal¶
When physical networks enable hairpin or similar behaviors, problems such as gateway check failure when creating Pods and abnormal network communication of Pods may occur. This is because the default MAC learning function of OVS bridge does not support this kind of network environment.
To solve this problem, it is necessary to turn off hairpin (or modify the relevant configuration of physical network), or update the Kube-OVN version.
When there are a large number of Pods, gateway check for new Pods fails¶
If there are a large number of Pods running on the same node (more than 300), it may cause packet loss due to the OVS flow table resubmit times exceeding the upper limit of ARP broadcast packets.
2022-11-13T08:43:46.782Z|00222|ofproto_dpif_upcall(handler5)|WARN|Flow: arp,in_port=331,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=00:00:00:25:eb:39,dl_dst=ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff,arp_spa=10.213.131.240,arp_tpa=10.213.159.254,arp_op=1,arp_sha=00:00:00:25:eb:39,arp_tha=ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
bridge("br-int")
----------------
0. No match.
>>>> received packet on unknown port 331 <<<<
drop
Final flow: unchanged
Megaflow: recirc_id=0,eth,arp,in_port=331,dl_src=00:00:00:25:eb:39
Datapath actions: drop
2022-11-13T08:44:34.077Z|00224|ofproto_dpif_xlate(handler5)|WARN|over 4096 resubmit actions on bridge br-int while processing arp,in_port=13483,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=00:00:00:59:ef:13,dl_dst=ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff,arp_spa=10.213.152.3,arp_tpa=10.213.159.254,arp_op=1,arp_sha=00:00:00:59:ef:13,arp_tha=ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
To solve this issue, modify the OVN NB option bcast_arp_req_flood to false:
kubectl ko nbctl set NB_Global . options:bcast_arp_req_flood=false
Created: June 30, 2022